Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. This statement is true not only in relation to people, but also to animals, and in particular - domestic chickens and broilers. The article will talk about Metronidazole, a drug widely used in veterinary practice as a prophylactic and therapeutic agent against serious ailments.
Release form and composition of "Metronidazole"
"Metronidazole" (the second name is "Trichopolum") for use as a medicine in veterinary medicine is available in two forms - in tablets and granules.
- Tableted. Each tablet contains 25% or 50% of the active substance metronidazole. Release form - 0.25 g, 0.5 g, 1.0 g. Packed in dense paper boxes or plastic cans of 100, 250 and 1000 pieces.

- Granular. Granules of white color with a shade of yellow or green in color, containing 25% of the active substance. Packed in film bags of 0.25, 0.50 and 1.00 kg.
Excipients that are contained in both forms of release are:
- starch;
- lactose;
- calcium stearate.
Important! "Metronidazole" is not embryotoxic (does not cause embryo death), teratogenic (does not provoke the development of abnormalities and malformations in the embryo) and hepatotoxic (does not cause functional and structural changes in the liver).
Pharmacological properties
The drug "Metronidazole" is detrimental to many types of protozoa, such as:
- histomonads;
- Giardia
- Trichomonas;
- balantidia;
- amoeba and others
The mechanism of action of Metronidazole is that protein nitro groups are blocked, a redox balance is disturbed in the cells of pathogenic microorganisms, which leads to an increase in the level of toxic products. Due to the interaction of toxins with protozoa DNA, the death of the latter occurs. The drug, absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, enters the body tissues and organ systems. The accumulation of the active substance occurs in the liver. Through urination, partially with feces, it is excreted from the body after 24–48 hours (in the form of metabolites and in its original form).
The drug, absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, enters the body tissues and organ systems. The accumulation of the active substance occurs in the liver. Through urination, partially with feces, it is excreted from the body after 24–48 hours (in the form of metabolites and in its original form).
Did you know? The English ornithologist J. Edgar proved that chickens are capable of experiencing empathy. If the offspring is worried for any reason, mother chickens also experience stress; they are sad when a chicken is lost or dies.
What diseases is Metronidazole used for?
In veterinary medicine, the aforementioned drug is used in the treatment of a huge number of diseases caused by bacterial infections and parasitic lesions. In poultry farming in relation to chickens, broilers, laying hens, Metronidazole is indicated for three diseases:
- Trichomoniasis (trichomoniasis) - A disease caused by protozoa Trichomonas. Infection occurs through water and feed. It spreads rapidly within the population, the incubation period is from three to four days to a week. It proceeds both in acute and in chronic forms. The acute course of the disease manifests itself in chickens in the form of apathy and drowsiness, loss of appetite due to diphtheria symptoms, lameness. Also, their feathers become tousled, their wings hang. From the gastrointestinal tract, frequent loose stools, feces of pale yellow color, liquid, with a pungent odor are observed. In the oral cavity there is a coating of curd consistency, when removed, deep ulcerations are detected. This nature of the lesion affects all internal organs of chickens. In especially severe cases, the perforation of the walls of one or another organ occurs, provoking fatal complications - sepsis, peritonitis, pericarditis. The contours of the liver increase in size, the structure of the organ changes.
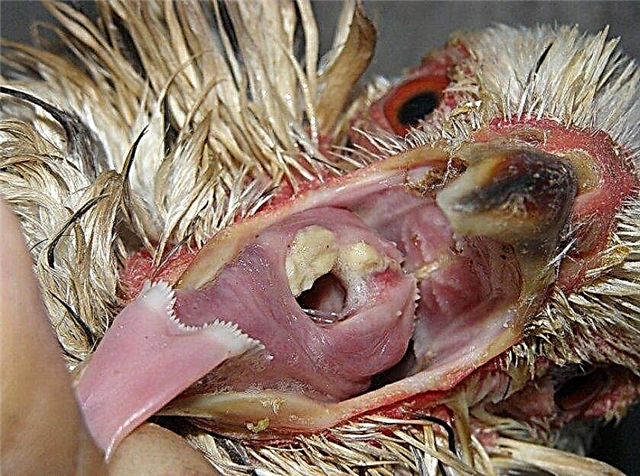
- Coccidiosis - a disease that is triggered by unicellular from the Coccidia squad, is invasive in nature (transmitted through inventory, feed, and drinking). Of particular danger for chickens, since at first the birds look healthy, and then there is a sharp deterioration in their health and death. Symptoms are largely similar to trichomoniasis - loss of appetite, feather cover changes, diarrhea with an admixture of blood appears. If laying hens get sick, then they stop the laying process. A clear symptom of the disease is that bird carcasses acquire a blue tint.
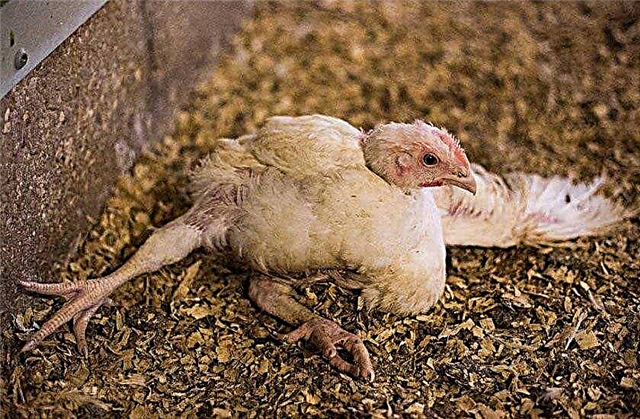

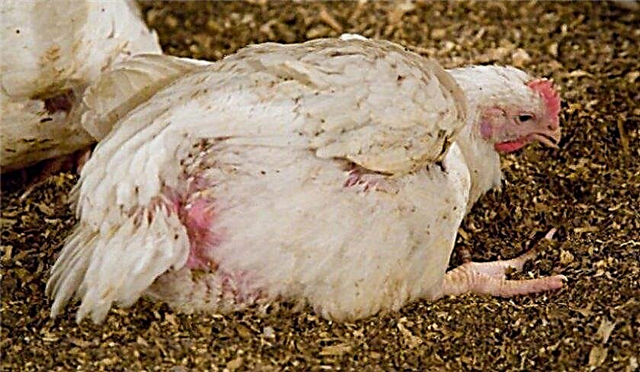
- Histomonosis (typhiohepatitis, enterohepatitis) - Infectious disease caused by protozoa Histomonas mellagridis. The household name is black head. It poses a special threat to young animals. Infection occurs as in the case of coccidiosis and trichomoniasis. The carriers of histomonads are earthworms. The course of the disease can be acute and chronic. The acute nature of the disease is more inherent in young birds and is characterized by a decrease in motor activity, lack of appetite. Their feathers begin to sag, the body temperature decreases, and diarrhea begins. Blood stagnation occurs, from which the scalp acquires a black color. Adults suffer from a chronic form of histomonosis, which causes thinness, general weakness.
Instructions for use
Upon identification trichomoniasis begin immediate treatment of the bird, adding the drug "Trichopolum" at a dosage of 3 g per 1 liter of drinking water. To clean the oral cavity from secretions and subsequent instillation, the concentration of the solution is changed - 17 g of the drug is dissolved in a liter of water. Plaque is removed using a swab soaked in a medicinal product. Medical events must be performed within 1 week.
Important! As a prophylaxis of the above diseases, it is recommended to contain young bird separately from the main stock.
For the prevention of this disease, contacts of chickens with pigeons should be excluded (almost 100% of pigeon individuals are carriers of infection), sick birds are urgently removed from the chicken coop, the premises and all surfaces of which are thoroughly disinfected. In addition, it is important to maintain the immunity of poultry with vitamin complexes, introducing them into the diet.
Because the coccidiosis young birds are susceptible, as a preventive measure for broiler chickens, once every two weeks, the drug should be added to the feed, at the rate of about 25 mg per 1 kilogram of live weight of the bird for 5 days. At histomonosis "Metronidazole" is introduced into the feed for 5-7 days. How much drug should be used is simple to calculate: the value of the required single dose is 0.05% of the feed weight.
At histomonosis "Metronidazole" is introduced into the feed for 5-7 days. How much drug should be used is simple to calculate: the value of the required single dose is 0.05% of the feed weight.
Contraindications and Precautions
During the entire period of use of Trichopolum, poultry specialists did not reveal any contraindications for the use of this drug. As with any drug, there is a risk of individual intolerance, which is very rare.
Did you know? The inhabitants of the chicken coop possess the intellect, which makes it possible to recognize and keep in memory the distinctive features of about a hundred individuals - both their relatives and people. Moreover, they remember who treats them well and who treat them badly.
Possible side effects after application
Allergic manifestations can occur as a side effect of the drug. As for the question of whether it is possible to avoid unexpected reactions to the use of the drug, the answer is positive - you should carefully monitor the condition and behavior of the inhabitants of the house and, at the slightest manifestations, discontinue the drug. A veterinarian will help you choose a medicine of a similar action, but with a different composition.
Shelf life and storage conditions
"Metronidazole" is suitable for use within 24 months from the date of release. The drug is stored in a dry room at an air temperature not exceeding + 25 ° C, without access to sunlight. If you suspect a disease, as well as for the prevention of a particular ailment, you should contact a veterinarian who, on the basis of a visual examination and laboratory tests, will diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment. This fully applies to the drug “Metronidazole” (“Trichopol”) mentioned in the article, its forms and dosages.