Gladiolus (Gladiolus), despite its capriciousness and exacting care, is one of the most popular flowers among gardeners. There are a huge number of varieties of this flower, pleasing with its variety and magnificence. However, when growing it, flower growers often encounter quite dangerous diseases, leading to the loss of beautiful, expensive varieties. One of the most dangerous is rust. Having a fungal nature, it is able to hit a large number of flowers in a very short time and lead to their death. In the article we will tell you what preventive measures consist of, and what you need to do when the first signs of this disease appear in gladioli.
Diseases and pests of gladioli
Most often, gladioli are affected by fungi, viruses, and various pests that damage mainly plant bulbs. In order to quickly take measures and apply effective methods of treating a flower, it is important to find out the cause of its wilt in a timely manner.
Did you know? In the Middle Ages, corms of gladioli were used as a food product. Possessing high nutritional value, they were consumed in baked, fried and marinated form.
Fungal lesions
Spores of harmful fungi spread very easily when they enter plants with water or air.
The most common five fungal diseases of gladioli:
- Fusarium, manifested on the gladiolus bulb in the form of red-brown depressions clearly limited from healthy tissue. The disease is also reflected in the aerial part, as a result of which leaf growth worsens, subsequently they turn yellow (starting from the tips of the lower leaves and over the entire surface) and dry.

- Sclerotiniaaffecting the vascular system of gladioli. Initially small brown spots appear on the bulbs along the edge of the scales, which grow with the development of the disease to recessed dark brown spots. Leaves bulbs, stems and leaves to dry.

- Septoria (hard rot) penetrates the plant through soil, air, water. Signs of damage: maroon-brown spots on the bulb, then increasing and blackening. Later, the plots take the form of dents. The disease on the leaves manifests itself in the form of clearly defined brown-burgundy spots, light in the center. Over time, spots tend to grow and blacken. The affected leaves dry out and convex black dots appear in the center of the spots, representing the fruiting bodies of the pathogenic fungus.
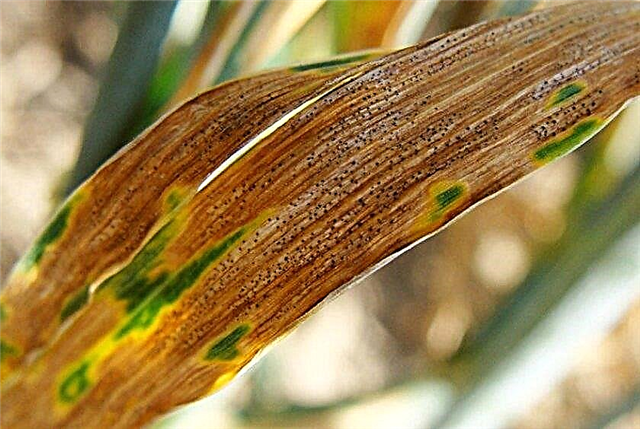

- Botritiosis, or gray rot, most often affects gladioli in cool, wet weather. The disease is dangerous for its rapid development. Sometimes it takes only a few days to infect the entire garden. Characteristic is the defeat of the whole plant. On the leaves, botrythiosis is manifested by small brown-red spots with a bright border, increasing in size. The flowers may become gray spots, which are spores of the fungus. Gray rot appears on the stem, it becomes fragile, easily breaks. In the bulb, as a result of softening, the bottom falls through, it takes the form of a donut. Affected areas of corms are browned.

- Penicillosis, called blue rot, occurs when the rules for storage of gladioli bulbs are violated. Distinctive signs of the disease are brown dents in the region of the base, which with development acquire roughness and yellowish-gray color. If the temperature in the storage rises to + 20 ° С, a greenish-blue coating appears, indicating the sporulation of mushrooms. Small balls are formed inside the bulb infected with penicillosis - sclerotia.

Viral lesions
Diseases caused by viruses are characterized by rapid development, and success in combating them depends on the timeliness of the measures taken.
They can have various manifestations:
- spotting on flowers and leaves;
- twisting of leaves and flowers;
- corm deformation;
- discoloration of flowers;
- crushing plants;
- overgrowth of shoots.
The most common carriers of viruses are insects, but there is always a risk of planting infected corms in the garden.
Important! In the first months of growing children of gladioli, all specimens lagging behind in growth, as well as curved and having any defects, should be dug up and removed from the flower garden. Even if they are not carriers of viruses and fungi at the moment, having a weak immunity, they can cause infection of the entire mass of plants.
The most dangerous viral diseases affecting gladioli are:
- Mosaic Beans - manifests itself in the appearance of an angular spotting of light green or dark green color. The flowers of the plant may become lighter or darker.

- Asthma Jaundice Virus - leads to yellowing of young specimens, starting from the tips of the sheets. Such leaves die off, after which the flowers are affected, which acquire a spiral shape and curl. The appearance of the bulbs does not change, but the plants grown from them have an unhealthy and weak appearance.
- Mosaic of Cucumber - is a rather dangerous virus, leading to dwarfism of plants. Outwardly manifests itself in the form of white stripes on the leaves. On the petals of bright varieties - in the form of yellowish stripes, silver-blue or purple spots.

- Tobacco Rattles and Tomato Ring Spots - have common symptoms. They lead to impaired plant development, curvature of the leaves and the appearance of chlorotic spots or stripes on them, as well as fringes.

Pests
The flower is most often damaged:
- Thrips - is a flying insect. Larvae and adult individuals sucking sap from plants are harmful. You can determine the defeat of this pest by whitish spots on the leaves, which subsequently dry up. Affected insect buds often do not open. Corms thrips dry out.

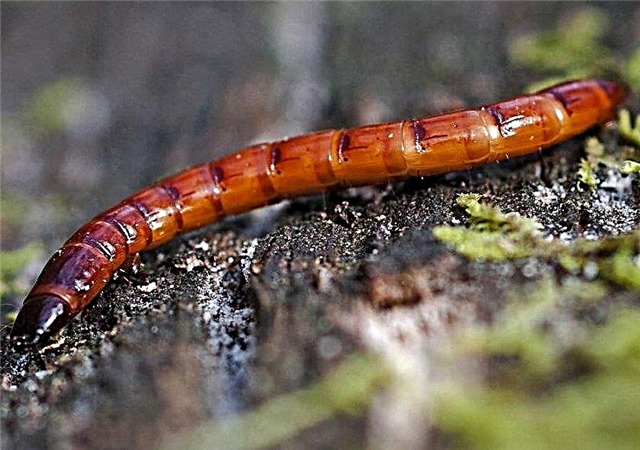
- Wireworms - Nutcracker beetle larvae resembling yellow caterpillars. They lead to the death of the plant, penetrating the bulb or the underground part of the stem.

- Aphid - It is a small insect of green color, sucking juice from a flower and carrying viruses.

- Garden scoop - It is dangerous because its caterpillars eat buds and sheets of gladioli.
Video: how to beat a scoop
What are the defects?
Beginning flower growers often encounter problems that are not related to the defeat of gladioli by viruses, fungi or pests:
- Curvature. Gladioli grow with curved stems and peduncles and bend to the ground. This happens for several reasons. For example, due to insufficient deepening of the bulbs. The optimum planting depth of corms is 15 cm. If this condition is not met, when the top layer of the soil dries up, the plant has a moisture deficit, it becomes more difficult to keep the green mass and it becomes woody. To preserve moisture, it is recommended to use mulching. A defect can also occur due to a lack of calcium or an excess of nitrogen. In this case, one can observe the friability of the stem, which is bent under the weight of peduncles. Plants can be helped by feeding them with calcium nitrate or potassium phosphate.

- Despite an apparently healthy and strong plant, peduncles do not appear. The reason may be a violation of the storage conditions of planting material (too low or high humidity and temperature, insufficient ventilation of the storages). But even with proper storage, expensive imported varieties do not always bloom in the first 2-3 years. This is due to the period of adaptation to the conditions of the region. If the soil is sparse with minerals, it is necessary to fertilize gladioli in a timely manner in order to obtain abundant and timely flowering. A long period of low temperatures and high humidity can also be one of the reasons for the lack of peduncles.
- Gladioli bloom too fast. On average, a gladiolus flower blooms 10 days. This period may be shortened due to a lack or excess of moisture in the soil and air or due to insufficient nutrition.

Why do gladioli have red leaves and flowers dry
Many gardeners were faced with the appearance of red spots on the leaves. Their development is facilitated by long periods of cold rainy weather.
Important! Infection of plants often occurs when the conditions for the content of seeds are violated, therefore, it is necessary to periodically inspect the corms for damage by harmful microorganisms and remove them in a timely manner, and carry out preventive treatment with healthy specimens with fungicides.
You can distinguish this disease from others by the following features:
- at the base of leaves orange or brown spores accumulate in pustules, from which spores of a color resembling rust fly out after cracking;
- yellow round or oval spots appear on the outer surface, gradually turning into stripes;
- in the absence of measures aimed at combating rust, it can cover the entire surface of the foliage, which first turns yellow, later blackens and crumbles;
- buds and inflorescences dry.
 If the listed symptoms are noticed on gladioli, one can say with confidence about the defeat of the flower by rust, caused by basidiomycetes, which provoke diseases of bulb and corm plants.
If the listed symptoms are noticed on gladioli, one can say with confidence about the defeat of the flower by rust, caused by basidiomycetes, which provoke diseases of bulb and corm plants.
Rust and how to deal with it
Rust is caused by Heterobasidiomycetes class fungi that infect plant tissues, sucking juice from them.
There are two types of fungi:
- co-ownerliving the entire life cycle on one plant instance;
- heterogeneousparasitic at the same time on two plants and considered the most dangerous.
The fungus is characterized by great survivability and can be transported both by air and by insects over great distances. Getting on a plant, the fungus takes away nutrients from it, destroying it from the inside. The disease spreads very quickly due to the large number of simultaneously maturing spores. Their number can be up to several tens of billions. Both wild-growing and cultivated plants, including ornamental ones, can rust.
Did you know? In ancient Greece, gladiolus was considered a weed, most often growing in wheat fields. They were uprooted and burned to prevent spread.
The causative agent of rust of gladioli is Puccinia iridis. On the corm, the disease manifests itself in the form of reddish dots extending deep into it. A lot of brown vesicles appear on the leaves of gladioli, which lead to their rapid yellowing and drying. In autumn, on the affected parts of the plant, black stripes can be seen, indicating that the fungus hibernated.
 Puccinia iridis
Puccinia iridis
The most favorable conditions for the development of Puccinia iridis are:
- sudden changes in temperature (day and night);
- cool weather;
- high rainfall;
- frequent fogs;
- severe thickening of the site and the presence of weeds;
- excess nitrogen in the soil.
Despite the danger of the fungus, you can fight it, and the sooner, the more chances to save the plants. If affected plants are found, they must be cut off, dig out and burn onions to prevent the spread of spores. The remaining plants should be treated with antifungal drugs.
Effective rust destroying agents are:
- Cumulus
- "Flint is old";
- "Coronet";
- Bordeaux liquid;
- Falcon;
- Oksikhom;
- copper chloride.
For the treatment of gladioli, it is recommended to use 1 or 2 percent solutions of the drugs in accordance with the instructions.
Supporters of alternative methods recommend such formulations as effective means:
- In water (4.5 L) dissolve 1 tbsp. l soda, 1 hour dishwashing detergent (gel), 1 tbsp. vegetable oil, 1 tablet of aspirin. Spray the resulting solution with flowers every 10 days.
- A third of a bucket of fresh manure pour water and insist for three days, stirring occasionally. Filter the resulting composition through a cloth and dilute with water in a ratio of 10 parts water to 1 part manure solution. Plants must be sprayed each time with a fresh composition before sunset.
- Many gardeners confirm the effectiveness of iodine against Puccinia iridis. To do this, 10 ml of a 50% solution of iodine is mixed in a ten-liter bucket of water. After the first treatment, re-spraying is carried out after 3 days.
Disease prevention
In order for gladioli to please with abundant and prolonged flowering, it is necessary to observe the rules for storing planting material, the rules for planting plants, as well as preventive measures to prevent diseases of both fungal and viral nature:
- Watering plants should be root. It is important to avoid getting water on leaves and flowers.
- Infected plant parts must be cut immediately. and burn or dig deep into the soil away from the site.
- When storing is important inspect seed regularlytreat with fungicides. Isolate and dispose of infected bulbs.
- Thoroughly clean the area in autumn, cleansing it of fallen leaves, fruits and broken shoots.
- Before planting, deeply dig a plot to destroy pathogenic spores wintering in the soil.
- Make potash and phosphorus fertilizers on time. Feed gladioli with minerals to strengthen immunity.
- Perform preventive treatment early spring fungicides.
- Along the perimeter of the site to plant dense shrubsthat will prevent the entry of pathogenic spores from the surrounding areas.
- Keep the flower garden clean, timely get rid of weeds, which are often carriers of the disease.
 Rust is a complex ailment requiring emergency measures to protect healthy plants. In order to prevent mass death of gladioli, it is necessary to regularly examine them and, when the first symptoms appear, take measures. It is also important not to forget about preventive measures aimed at strengthening the immunity of plants and protecting them from damage by pathogenic microorganisms and pest attacks.
Rust is a complex ailment requiring emergency measures to protect healthy plants. In order to prevent mass death of gladioli, it is necessary to regularly examine them and, when the first symptoms appear, take measures. It is also important not to forget about preventive measures aimed at strengthening the immunity of plants and protecting them from damage by pathogenic microorganisms and pest attacks.