Rotting onions on the site and during storage is a problem that no gardener is safe from. Before planting a crop, it is important to know how to act in a similar situation. Read on to see why bulbs rot and how to preserve crops.
The main causes of decay
In addition to diseases and pests, onion rot has four reasons: excess moisture, improper crop rotation, an abundance of nitrogen in the substrate, and infected seeds before sowing.
Did you know? Onions are used not only for food. There are different varieties of decorative onions that are grown for landscaping.
Excess moisture
Watering is one of the most important measures in the care of onions. Moderate hydration is good for the crop, but excessive watering is harmful.
Farmers often make the following mistakes in growing onions:
- ridges are watered more often than 1 time in 4–7 days;
- 1 m² use more than 35 liters of water;
- irrigate the soil even in the rainy season;
- do not wait for the drying of the top layer of the substrate;
- planted in heavy soils with high clay content;
- arrange ridges in places with high groundwater;
- do not undermine the soil;
- continue watering 3-4 weeks before harvesting.
Crop rotation failure
Experienced gardeners are sure to think about crop rotation before planting. Different cultures take different nutrients from the soil. If you plant onions every year in one place, the soil will be depleted. For 2-3 years of planting, the plant no longer receives the right amount of useful elements. As a result, the bulbs grow less strong, including rotting. Accordingly, the farmer must wait 3-4 years before planting the onions in the same place.
In addition, improper crop rotation reduces the resistance of onions to diseases and pests. Infections and insects, in turn, also provoke fruit rot.
Did you know? The three world leaders in growing onions include China, India and Egypt.
Excess nitrogen in the soil
Fertilizers in the right doses improve the condition of the plant. Violation of the fertilizing technique is fraught with rotting onions. An excess of nitrogen is especially dangerous for vegetables.
In the early stages of growth, nitrogen is extremely important, but it cannot be introduced throughout the growing season. Mineral fertilizing is regulated by the farmer himself, but inexperienced summer residents have problems with organic matter, for example, when fertilizing with fresh manure. This organic fertilizer releases a lot of nitrogen. The vegetable, which is fertilized with manure, grow large feathers, but the bulb itself does not have time to form. There is no ripening, from which the vegetable begins to rot even in the soil. As a result, the farmer does not collect from the garden a healthy vegetable, but spoiled onion heads.

Infected planting material
The quality of planting material affects the crop. Seeds that have not been disinfected can be infected with a fungus, bacteria or viruses. In instances of sevka, larvae of harmful insects can be found. If you do not disinfect the material, diseases will begin to develop - as a result, the plant will be weakened, and the crop will begin to rot even in the beds.
Diseases and pests that cause rot
Diseases and pests are the most dangerous for growing onions. They not only spoil the crop, but can infect neighboring crops. To cure plantings, the gardener needs to immediately determine the disease and begin to solve the problem.
Disease
Diseases are caused by harmful infectious agents that were in the soil and planting material or were in the beds during the growth of vegetables. Rotting can be caused by bacterial soft rot, onion bacteriosis, cervical rot, white rot, fusarium or powdery mildew.
Bacterial soft rot
The causative agent of the disease is a bacterium that settles on a mature onion. You can identify the disease closer to the harvest.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- improper watering;
- temperature differences;
- lack of top dressing or their deficiency.
- 2-3 plates rot inside the bulb;
- affected parts turn yellow, sandy or grayish;
- there is a fetid odor;
- plates that are not affected by rot look completely healthy.

Onion bacteriosis
Onion bacteriosis is a bacterial disease, which, like the previous one, is more often determined in the last ripening period.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- loose fit due to improper care;
- excessive watering;
- dampness of the soil.
- the head rots from the middle;
- rot is gray, often color is closer to brown;
- affected areas are soft and slippery to the touch;
- a putrefactive smell is felt;
- with the maximum degree of damage, the entire bulb rots.
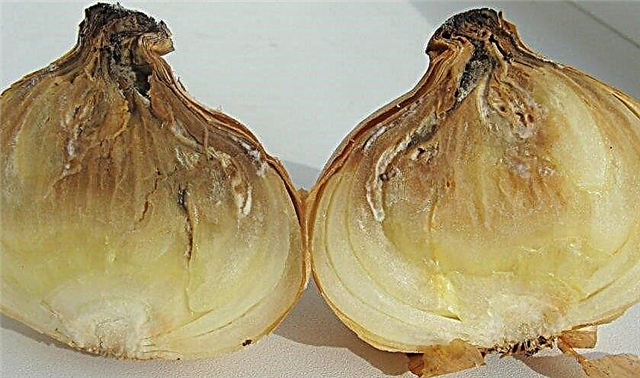
Neck rot
Cervical rot is a fungal infection. Like the above diseases, it can be determined closer to the end of the growing season. Often it already appears in onions deposited for storage.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- untimely harvesting;
- wrong crop rotation;
- lack of seed treatment or sowing with fungicides;
- frequent rains;
- excessive watering.
- the neck of the bulb becomes soft;
- affected areas turn gray;
- the whole head is gradually covered with a grayish coating;
- fungal spores in the form of black inclusions are observed on the plaque.

White rot
White rot is caused by spores of the fungus.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- excessive watering at low temperatures;
- wrong crop rotation;
- a lot of nitrogen in top dressing;
- acidic soil.
Signs of the disease:
- feathers fade and turn yellow;
- a white coating appears on the bottom of the bulb;
- gradually plaque spreads over the entire outer shell of the vegetable;
- if you start the disease, the onion begins to rot from the inside;
- the rotten fruit dries up.

Fusarium rot
Fusariosis is a dangerous fungal disease that affects many garden crops, and onions are no exception.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- high air temperature;
- plentiful watering;
- frequent rains;
- onion fly attack.
Signs of the disease:
- feathers turn yellow, then lose their shape and die;
- the vegetable grows more slowly than usual;
- the roots of the bulb become brown, begin to rot;
- the bottom is covered with filamentous plaque;
- with excessive moisture in the rotting areas, pink blotches can be noticed;
- in a section the lower part of a grayish color and a watery consistency.

Powdery mildew
The causative agent of powdery mildew is a fungal infection. A disease can ruin an entire crop.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- high humidity;
- cold weather.
- feathers are covered with yellow spots;
- the shape of the feathers is lost;
- with increased humidity, a gray coating appears on the green part of the onion, sometimes with a lilac hue;
- after feathers, the head begins to rot;
- last of all, roots rot.

Pests
Pests often cause rotting bulbs. Among the most common - onion fly, stem and bulb nematode.
Onion fly
Signs of the appearance of an onion fly:
- yellow feathers;
- holes in feathers and bulbs;
- oviposition in lumps of soil.

Stem and bulb nematode
Signs of the appearance of stem and bulb nematodes:
- feathers grow thicker and shorter;
- leaves are covered with spots of sand color;
- Swelling appears on the feathers, after which they die off;
- the neck of the turnip softens.
- initially located in the soil;
- get on the seeds as an infection;
- infect plantings through irrigation;
- go to the plot on garden tools.
Worm larvae settle in the soil. From the ground, nematodes make their way into ripened bulbs. Infected onions soon change their appearance, in particular, rot.
Possible causes of rotting when stored at home
Sometimes a crop that does not rot on the beds spoils after harvest. It is normal if several copies become unusable, but mass rotting is a sign of a problem.
Agronomists identify several reasons why the vegetable is poorly stored:- the gardener has deposited early ripening varieties, which are best used as quickly as possible after harvesting;
- in the room where the crop is stored, ventilation is poor or absent;
- picking onions too early;
- the bulbs were in the ground longer than they were supposed to be;
- humidity in the room is above normal;
- the temperature regime is violated, and both high and low temperatures are harmful;
- in winter vegetables were frozen;
- the farmer put too many bulbs in one container;
- violated the rules for packing the crop for storage;
- damped bulbs are deposited;
- the product was not left to lie in the air before being placed in containers;
- the gardener removed healthy and diseased specimens from the garden, did not go through the crop, and put all the bulbs in one batch;
- during storage, diseases that could not be determined on the bed appear.
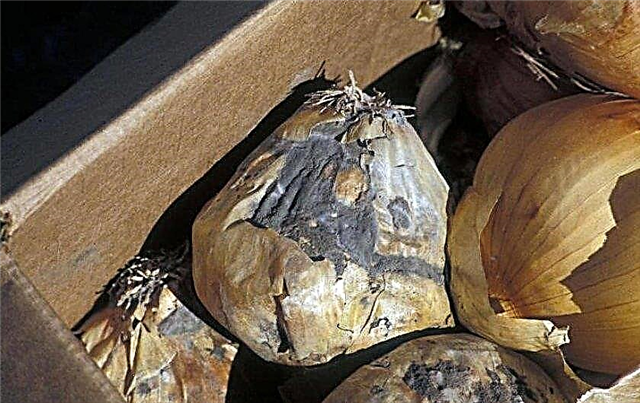

All factors, individually or in combination, cause decay. The farmer should reconsider the approach to storing onions and try to rectify the situation - otherwise the crop may rot completely.
Ways to combat diseases and pests
The first measure in treating rotting onions is to remove the affected vegetables.
Next, you should proceed from a specific disease. Depending on the pathogen, various drugs must be used:
| Disease | Treatment |
| Bacterial soft rot | To process with means of "Pergado R", "Kurzat R" or other preparations with copper in the composition |
| Onion bacteriosis | Pour planting 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid |
| Neck rot | Protect healthy plants with Bordeaux fluid or copper sulfate |
| White rot | Treat plantings with Ridomil Gold or Quadrice |
| Powdery mildew | Switch to nitrogen-free fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium, treat ridges with copper sulfate |
| Fusarium rot | Till the soil with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid |

Pests are also eliminated by chemical means.
For treatment, use the following tips from experienced gardeners:
| Pest | Treatment |
| Onion fly | Treat plantings with the preparation “Aktara”, “Tabazol” or “Medvetoks”. |
| Stem and bulb nematode | It is almost impossible to cure a culture. You can try to treat the beds with a nematicide, for example, Nematofagin BT or Peliomycin. |
Important! Before using a pesticide, pay attention to its compatibility with other drugs. So, the Peliomycin nematicide is not compatible with fungicides.
Preventative measures
In order not to waste your efforts on treatment, think about disease prevention before planting.
Gardeners call the following preventive measures:
- Crop rotation. In the area where onions were planted last year, it is better to plant beans, cabbage, potatoes, tomatoes or cucumbers. Onion plantings can be returned to their original place in 3-4 years.
- Choosing a landing place. In clay soils, especially where groundwater is close to the surface of the earth, water may stagnate. For planting onions, choose a looser soil. If this is not possible, put sand into the ground before planting.
- Disease resistance. Plant onion varieties resistant to diseases and pests. Modern breeders have bred a lot of these varieties of vegetables - among them Sturon, Texas Yellow, Centurion F1.
- Planting Material Processing. Certified products of official manufacturers from the packages can not be disinfected. Seeds and seeds are needed for disinfection, acquired from hand or received from your own garden. Treat the seeds with copper sulfate or potassium permanganate - the drugs will destroy the infections that are likely to be present in the planting material. Sevok needs to be inspected for damage - if there are areas with rot, plaque and other lesions, the material is thrown away. Only a holistic and healthy plant is suitable for planting. Before planting, some gardeners also withstand it in water with a temperature of at least + 40 ° C - this measure will help to eliminate the presence of pests.

- Tillage before planting. Before planting a seed set or sowing seeds, treat the soil with fungicidal solutions or potassium permanganate, which will help get rid of bacteria, fungus and insect larvae.
- Proper watering. Water the onion sparingly. The main rule in watering is to wait for the topsoil to dry out. Usually, onion plantings are watered no more than 1-2 times a week, pouring not more than 35 liters of water on 1 m². In rainy weather, humidification can be limited. One month before harvest, completely stop irrigation.
- Proper feeding. Nitrogen is needed at the very beginning of crop growth. As the onion grows, reduce the amount of nitrogen fertilizing. Do not use fresh manure for fertilizing. From organics compost will do.
- Soil care. Loosen the soil in a timely manner and remove weeds as they appear - this will prevent the water from stagnating and prevent rotting from excessive moisture.
- Preventive treatment of ridges. Pesticides will help prevent diseases and pests. So, treatment with fungicides, for example, “Trichodermin” or “Fitosporin”, eliminates the development of bacteriosis. From fungal diseases, prevention will be watering with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid. From nematodes to planting, add ammonia water, percalcite and urea to the soil. To prevent onion fly larvae from growing in the bulbs, it is necessary to decontaminate planting stock with Immunocytophyte.
- Inspect the landing. Timely remove rotten and damaged plants from the ridges - so the disease will not spread to other vegetables.

Equally important is prevention during storage of the crop.
To keep most of the onions intact, pay attention to the following measures:
- Store medium or late ripening varieties - it is better to eat early onions immediately.
- Do not pick onions ahead of time.
- Harvest immediately after ripening, do not leave it for a long time in the ground.
- After harvesting, leave the vegetables in the fresh air to dry.
- If there is a chance of rain or the air is too humid, transfer the crop to a dry place or under a canopy.
- Spread on drying the bulbs in one layer.
- Discard damaged and affected heads immediately; do not store with healthy specimens.
- Use containers with openings or mesh bags for storage.
- The optimum humidity in the room is 80–85%.
- Keep the temperature within 0 ... + 3 ° С.
- You can also keep the onions warm, withstanding a regime of +18 ... + 20 ° С.
- Store vegetables in the dark.
- In time, remove the heads that began to rot or wither.
Important! If only part of the bulb is affected, the product can be processed: cut the rot, and freeze or dry the whole part.
If the onion begins to rot in the garden or after harvesting, it is urgent to correct the situation. With the right actions, the gardener will be able to keep most of the vegetables healthy and intact.