Red boletus (redhead) is one of the most popular edible mushrooms. This species in the temperate zone is found almost everywhere, therefore it is considered a traditional seasonal product in many regions of Russia and the CIS countries. The article provides a detailed description of red boletus, as well as its basic properties and useful qualities.
Description
Redhead is one of the typical representatives of the genus Lekcinum of the Boletovye family. This is an edible species, which is often used not only for food, but also as the main ingredient in all kinds of infusions, decoctions and other medicines.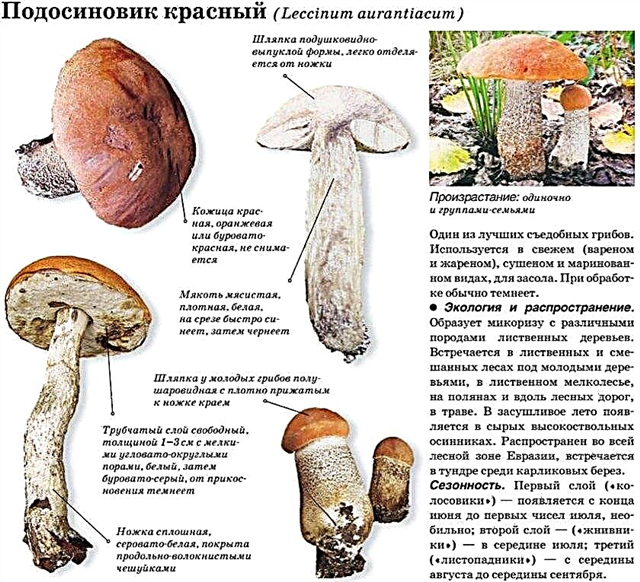
Leg
The leg of the fungus is cylindrical-conical in shape: at the level of the mycelium it is the thickest, and in the cap area it is slightly thinner. Its average length is 5–10 cm, but there are also large specimens with a stalk about 15 cm. Its thickness varies between 1–5 cm. The skin is covered with small longitudinal scales painted white, but as it grows, the hue becomes more brown.
Video: The growth of red boletus
Hat
The cap of the boletus is quite large (up to 15 cm in diameter), however, in some specimens its size can reach up to 30 cm. In young mushrooms, its shape is hemispherical, and the edges are bent inward. For adult fruiting bodies, a cap of a pillow shape is characteristic.
The upper integument is smooth, but can also be velvety, the skin from the pulp is practically not separated. The color of the hat can vary from light to brown-red shades. A characteristic feature of the skin color is that it varies depending on the growth site of the fungus, as well as the main symbiont tree.
Pulp
The flesh of the boletus is tender, while fleshy and quite elastic, but as it ages, it can become soft. The legs of the fabric are more rigid, fibrous. On the cut, the fungus is white, however, after tissue damage, they instantly turn blue, and then completely acquire a dark brown or black tone. Raw pulp has no saturated smell.
Spore layer
Gimenophore in a tubular type fungus. The tubules are freely located, their average length is within 1-3 cm. The shape of the pores of the tubules is round or angularly rounded. The color of the spore-bearing layer is predominantly white, but as it grows, it can acquire an olive, yellow or brown-yellow hue. After damage to the hymenophore, its main color instantly darkens.

Spore powder
Spores are predominantly spindle-shaped, rounded, with a smooth surface. Their average size is about 40 microns. The color of the spore powder can be various olive-brown tones.
Did you know? Mushrooms are one of the most unique life forms on Earth. They lead an attached lifestyle, like plants, but are not able to carry out photosynthesis, and use only organic substances for their nutrition (typical only for animals and insects).
Distribution area
The most common redhead can be found in young deciduous or mixed forest. The main species with which the species enters into mycorrhizal relations are poplar and aspen. You can also see the mushroom in the plantations of hornbeam, oak, beech, birch or willow, but this is quite rare. The most optimal climatic zones for it are the territories of the temperate zone of Eurasia, North America, as well as the Urals and the Caucasus.
Collection
The development of this fungus is observed from early June to late October. The most active growth of fruiting bodies begins in the first half of October, which is considered the season of mass gathering of redheads.
Video: Collecting boletus
Use
Red boletus can be called one of the most valuable forest products. It is distinguished by excellent taste characteristics, and is also able to saturate the body with easily digestible protein, vitamins and trace elements. In addition, often the mushroom is used as the main tool for the preparation of drugs against a whole complex of ailments.
For food
Boletus mushrooms are extremely tasty mushrooms, so they are great for preparing any dishes. Most often they are used as a fragrant base for soups and stews, including in combination with all kinds of vegetables. However, the most popular are fried mushrooms, in addition to potatoes or meat.
 For culinary purposes, the boletus leg is not recommended. It is excessively stiff, which can give the dishes an unpleasant aftertaste.
For culinary purposes, the boletus leg is not recommended. It is excessively stiff, which can give the dishes an unpleasant aftertaste.
For medical purposes
The main value of red boletus is the rich chemical composition of the pulp. This allows you to saturate the body with substances that can have a protective, restoring and anti-inflammatory effect.
- That is why all kinds of infusions, as well as mushroom powder are actively used in traditional and traditional medicine for the treatment of such diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- anemia
- nervous disorders;
- Depression
- chronic pathologies of the digestive system;
- digestive disorders associated with dysbiosis;
- oncological formations;
- dermatological diseases of the skin of the face.

Contraindications
Despite the proven benefits for the body and therapeutic effect, there are bans on the use of mushroom dishes. The main contraindications are liver and kidney pathologies, especially in the acute phase.
In addition, it is not recommended to abuse boletus, because their use in large quantities can cause digestive upset. It is recommended to abandon the redheads to the elderly, as well as children under 12 years old, in order to avoid a sharp allergic reaction of the body.Important! Pregnant women can use mushrooms exclusively in boiled or stewed form. Fried foods are overly difficult to digest, and pickled ones are useless, as long-term heat treatment destroys almost all the beneficial properties.
Difference from false boletus
Today in nature there is only one species that can be called a false boletus: the so-called mustard or gall mushroom. Despite the fact that it is not poisonous, its flesh has an unpleasant bitterness, which often makes mushroom dishes and preservation unsuitable for consumption. It is not difficult to distinguish mustard: it grows exclusively under coniferous plants, while boletus only under hardwood.
In addition, the main features of the bile fungus are the following:
- gimenofor has a pale pink tint;
- the leg is covered with a brown mesh pattern resembling snake skin;
- when cut, the white flesh acquires a pink hue.

Interesting Facts
Boletus can be called one of the most studied forest inhabitants. The most amazing facts about him are the following:
- in North America, a traditional wedding dish is prepared from boletus - stewed hats seasoned with cloves and all kinds of spices (serving such mushrooms to the newlyweds is customary in a new clay pot);
- redhead broth is saturated with protein, fatty acids and water-soluble vitamins, so its nutritional value is not inferior to meat broth;
- the largest fruiting bodies grow in the North and the Far East; mushrooms with a cap up to 40 cm in diameter are quite common here;
- the name of this species did not arise by chance, despite the fact that the fungus is able to establish mycorrhiza with almost all deciduous trees, the largest fruiting bodies are formed only in symbiosis with aspen.

Magical properties
From time immemorial, people have highlighted not only useful, but also the magical properties of boletus. It is believed that this fungus is able to actively accumulate negative energy from the environment. This feature is recommended to take into account mushroom pickers and harvest forest products exclusively in favorable areas, for example, away from geomagnetic fields.
Red boletus is a favorite mushroom of inveterate mushroom pickers, as well as ordinary lovers of forest delicacies. It is characterized by a unique and rich taste, as well as a number of medicinal properties. At the same time, the red boletus does not have toxic doubles, which makes it possible to attract even children to its collections.











